Conditional
Statements:
The
following are the conditional statements are available for decision making:
- If
- Switch
If-else:
If-else conditional
construct is followed by a logical expression where data is compared and a
decision is made on the basis of the result of comparison.
Syntax:
public
class example:
{
if (expression)
{
statements;
} else
{ statements };
}
Calculating Total interest
based on the given conditions:
Principle
Amount Rate of Interest
>=10,000 20%
>=8000&&<=9999
18%
<8000 16%
class IFCondition
{
public float princ,
nyrs, rate, interest;
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
IFCondition obj = new
IFCondition();
obj.res();
Console.ReadLine();
}
public void res()
{
Console.Write("\n
Enter Loan and No of Years");
princ = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
nyrs = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
if (princ >= 10000)
{
rate =
20;
}
else if (princ >=
8000 && princ <= 9999)
{
rate =
18;
}
else if (princ < 8000)
{
rate =
16;
}
interest =
princ * nyrs * rate / 100;
Console.Write("Years:{0}",
nyrs);
Console.Write("Loan:{0}",
princ);
Console.Write("Rate
of Interest:{0}", rate);
Console.Write("Interest
Amount:{0}", interest);
}
}
Switch case:
It is used when there are multiple
values for a variable.
public class example
{
switch (variable)
{
case ‘0’:
statements;
break;
. . . .
}
}
Simple Switch Case
Example:
class SimpleSwithch
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Calculator obj = new
Calculator();
obj.cal();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class Calculator
{
public int a, b,
sum,diff,mul,div;
public char c;
public void cal()
{
menu:
Console.Clear();
Console.WriteLine("=======================================");
Console.WriteLine("Menu");
Console.WriteLine("1.Addition");
Console.WriteLine("2.Subtraction");
Console.WriteLine("3.Multiplication");
Console.WriteLine("4.Division");
Console.WriteLine("=======================================");
Console.WriteLine("Enter Your Option");
c = Convert.ToChar(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter the Values of a,b");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch
(c)
{
case
'1':
sum = a + b;
Console.WriteLine("{0}", sum);
break;
case
'2':
diff = a - b;
Console.WriteLine("{0}", diff);
break;
case
'3':
mul = a * b;
Console.WriteLine("{0}", mul);
break;
case
'4':
div = a / b;
Console.WriteLine("{0}", div);
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("Enter M for Menu or Any other key to Exit");
c = Convert.ToChar(Console.ReadLine());
if
(c == 'M')
{
goto
menu;
}
}
}
Loop
Structures:
- For
- While
- Do- While
(a)
for loop:
Syntax:
for( initialization; termination; increment/decrement )
class forloop
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
implement
obj = new implement();
obj.forloop();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class implement
{
public void forloop()
{
Console.WriteLine("The Output is displayed by using
Console.WriteLine()\n");
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}", i);
}
Console.WriteLine("\nThe Output is displayed by using
Console.Write()\n");
for
(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.Write("{0}\t", i);
}
}
}
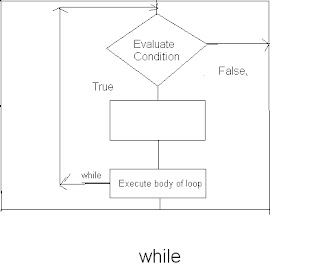
while loop
Syntax:
while ( expression )
{
statements;
}
do – while loop
Syntax:
do
{
statements;
}
while ( expression )
{
statements;
}


No comments:
Post a Comment